The Comprehensive Ultimate Guide to Understanding and Choosing the Right Press Brake
In the world of metal fabrication, the press brake stands out as an essential piece of machinery for bending and shaping metal sheets. For anyone involved in manufacturing, whether you're a seasoned professional or just starting out, understanding the intricacies of press brakes is crucial to enhancing operational efficiency and product quality. This comprehensive ultimate guide aims to demystify the process of selecting the right press brake for your specific needs.
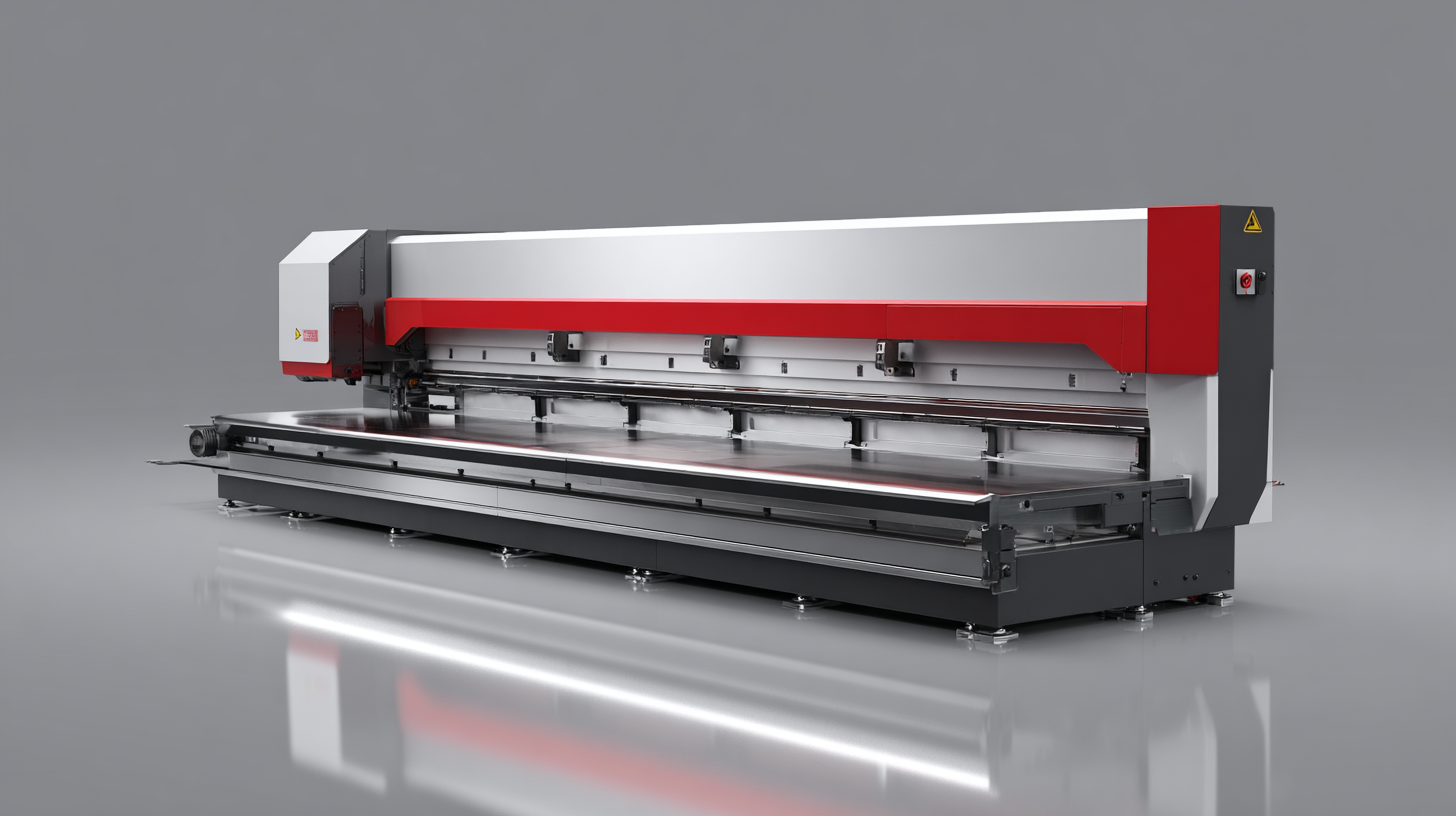 We will explore different types of press brakes, their key features, and factors to consider when making your decision. By the end of this tutorial, you will be equipped with the knowledge needed to choose the best press brake that aligns with your production goals and enhances your fabrication processes.
We will explore different types of press brakes, their key features, and factors to consider when making your decision. By the end of this tutorial, you will be equipped with the knowledge needed to choose the best press brake that aligns with your production goals and enhances your fabrication processes.
Understanding the Different Types of Press Brakes Available in the Market
When it comes to understanding the different types of press brakes available in the market, it’s essential to recognize that not all machines are created equal. Press brakes are classified into several categories, with hydraulic, hybrid, and servo-electric types being the most prevalent. Hydraulic press brakes are known for their robust capabilities and versatility, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. They operate using hydraulic fluid to generate force, allowing for precise bending of metal sheets.
On the other hand, hybrid and servo-electric press brakes represent the shift toward more energy-efficient solutions. Hybrid models combine hydraulic and electric drive systems, optimizing power consumption while maintaining performance. Servo-electric press brakes, entirely electric, provide unparalleled precision and reduced energy costs, appealing to manufacturers focused on sustainability and operational efficiency. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for businesses seeking to invest in the right press brake that aligns with their production needs and environmental goals.
The Comprehensive Ultimate Guide to Understanding and Choosing the Right Press Brake
Key Features to Consider When Selecting a Press Brake
When selecting a press brake, understanding the key features is pivotal to making an informed decision. One of the foremost considerations is the machine's capacity, which refers to the maximum tonnage it can handle. Depending on your specific bending requirements, this capacity will determine your ability to work with various materials and thicknesses. Moreover, the type of drive system—whether hydraulic, mechanical, or electric—also plays a crucial role in the performance and efficiency of the press brake. Hydraulic models tend to offer greater flexibility, while electric designs provide precision and energy savings.
Another important factor to evaluate is the tooling versatility of the press brake. Different bending operations may require various dies, and having a machine compatible with a wide range of tooling can enhance its functionality. Additionally, look for features such as CNC controls, which allow for greater automation and repeatability, making complex bends easier and more accurate. An intuitive control system can significantly reduce setup time and increase productivity. Finally, don’t overlook the build quality and safety features of the press brake, as these aspects will ensure reliability and protect the operators during operation.
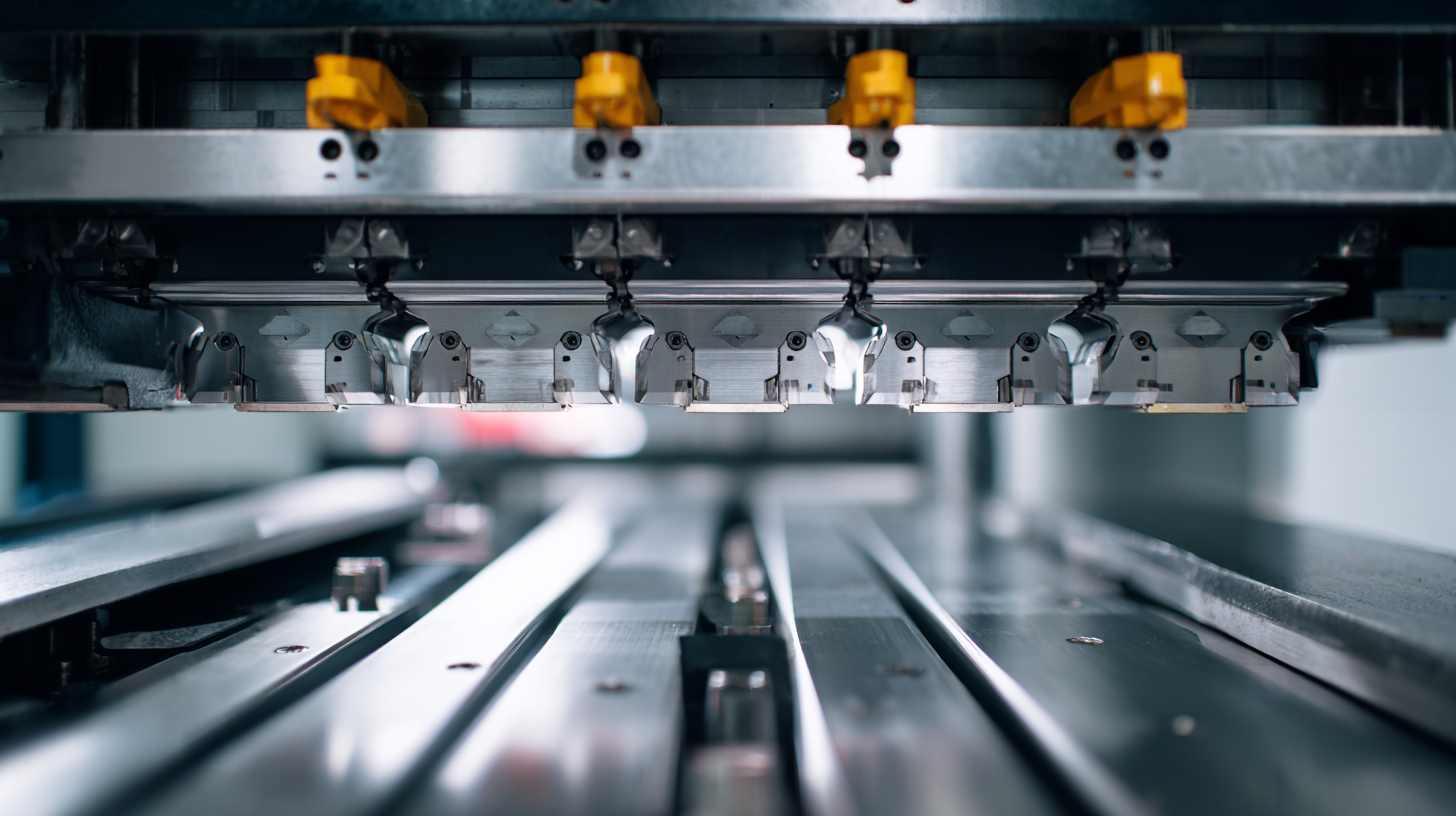

Comparing Mechanical vs. Hydraulic Press Brakes: Which is Right for You?
When it comes to choosing between mechanical and hydraulic press brakes, the decision largely depends on your specific manufacturing needs. Mechanical press brakes are generally known for their speed and precision, which makes them ideal for high-volume production tasks. They utilize a toggle mechanism that can deliver rapid bends with consistent accuracy. However, these machines may have limitations in terms of the material thickness that can be handled effectively.
On the other hand, hydraulic press brakes offer exceptional versatility and are better suited for handling thicker materials. Their design allows for more control over force and bending angle, which can be a significant advantage for complex or custom fabrication projects. Hydraulic systems can adapt to various materials, providing more flexibility in operation.
**Tips:** When deciding between the two types, consider the specific applications you need the press brake for. If your projects require diverse material handling and heavy-duty jobs, a hydraulic press brake may be the way to go. Conversely, if speed and efficiency in a less variable production run are what you need, a mechanical press brake could be more suitable. Always evaluate the required precision and the range of materials you plan to work with before making your selection.
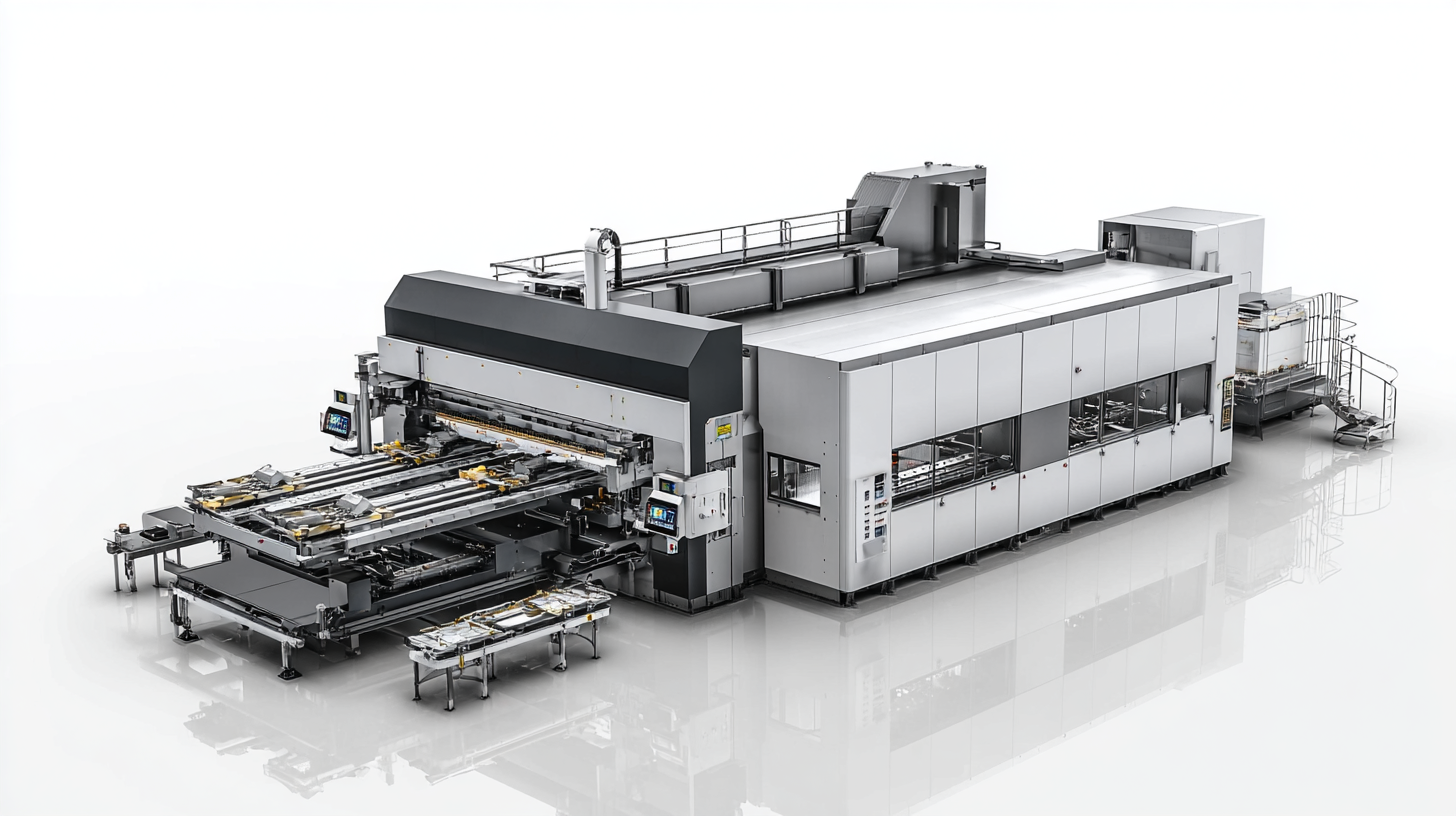
Exploring CNC vs. Manual Press Brakes: Pros and Cons
When it comes to choosing the right press brake, understanding the differences between CNC and manual press brakes is essential.
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) press brakes offer a high level of automation and precision, making them ideal for complex and high-volume production environments.
According to a 2021 report by IBISWorld, the CNC machinery sector is expected to grow at a rate of 3.5% annually, highlighting the increasing reliance on automated processes in manufacturing.
The ability to program intricate bending sequences and ensure repeatability often outweighs the initial investment costs for businesses focused on efficiency and accuracy.
On the other hand, manual press brakes are favored for their simplicity and lower upfront costs, making them a practical choice for smaller businesses or shops that deal with custom, one-off projects.
A study by MarketWatch indicates that manual press brakes represent about 35% of the press brake market, particularly appealing to craftsmen who value hands-on control over their work.
While they require skilled operators and can lead to variations in results, their adaptability to various bending tasks and materials allows for flexibility, which is critical in niche markets.
Ultimately, the choice between CNC and manual press brakes hinges on specific operational needs, budget constraints, and production volume.
Maintenance Tips to Maximize the Lifespan of Your Press Brake
Press brakes are essential machinery in metal fabrication, and maintaining them is crucial to maximizing their lifespan. Regular maintenance is akin to the diligent care required to extend the life of a vehicle. Just as comprehensive vehicle upkeep can help a car reach milestones like 300,000 miles, consistent servicing of a press brake can prevent premature wear and enhance efficiency. According to industry reports, machinery that undergoes regular maintenance can experience a lifespan increase of up to 50%, significantly reducing replacement costs and downtime.
Integral to press brake longevity are routine inspections of electrical systems, hydraulic fluids, and tooling. Ensuring that the hydraulic fluid is clean and at proper levels can prevent overheating and excessive wear. Additionally, monitoring the alignment and calibration of the machine can prevent inaccuracies in bending, thereby preserving the integrity of both the press brake and the materials being worked on. Implementing a standard maintenance schedule, similar to the systems in agricultural machinery that utilize separate oils and filters for different components, allows operators to track wear and address potential issues before they escalate.
The Comprehensive Ultimate Guide to Understanding and Choosing the Right Press Brake - Maintenance Tips to Maximize the Lifespan of Your Press Brake
| Dimension | Value |
|---|---|
| Press Brake Type | Hydraulic |
| Bending Capacity | 50 tons |
| Max Bending Length | 3 meters |
| Tooling Type | Standard V-Die |
| Operating Pressure | 210 bar |
| Maintenance Frequency | Quarterly |
| Lifespan Expectancy | 10-15 years |
| Common Issues | Hydraulic leaks, Misalignment |









